How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank.
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
1. Which action is performed by a client when establishing communication with a server via the use of UDP at the transport layer?
2. Which transport layer feature is used to guarantee session establishment?
3. What is the complete range of TCP and UDP well-known ports?
4. What is a socket?
5. A PC is downloading a large file from a server. The TCP window is 1000 bytes. The server is sending the file using 100-byte segments. How many segments will the server send before it requires an acknowledgment from the PC?
Explanation: With a window of 1000 bytes, the destination host accepts segments until all 1000 bytes of data have been received. Then the destination host sends an acknowledgment.
Explanation: Window is the number of bytes that the sender will send prior to expecting an acknowledgement from the destination device. The initial window is agreed upon during the session startup via the three-way handshake between source and destination. It is determined by how much data the destination device of a TCP session is able to accept and process at one time.
7. What does a client do when it has UDP datagrams to send?
Explanation: When a client has UDP datagrams to send, it just sends the datagrams.
8. Which three fields are used in a UDP segment header? (Choose three.)
Explanation: A UDP header consists of only the Source Port, Destination Port, Length, and Checksum fields. Sequence Number, Acknowledgment Number, and Window Size are TCP header fields.
9. What are two roles of the transport layer in data communication on a network? (Choose two.)
Explanation: The transport layer has several responsibilities. The primary responsibilities include the following:
10. What information is used by TCP to reassemble and reorder received segments?
Explanation: At the transport layer, TCP uses the sequence numbers in the header of each TCP segment to reassemble the segments into the correct order.
11. What important information is added to the TCP/IP transport layer header to ensure communication and connectivity with a remote network device?
12. Which two characteristics are associated with UDP sessions? (Choose two.)
Explanation:

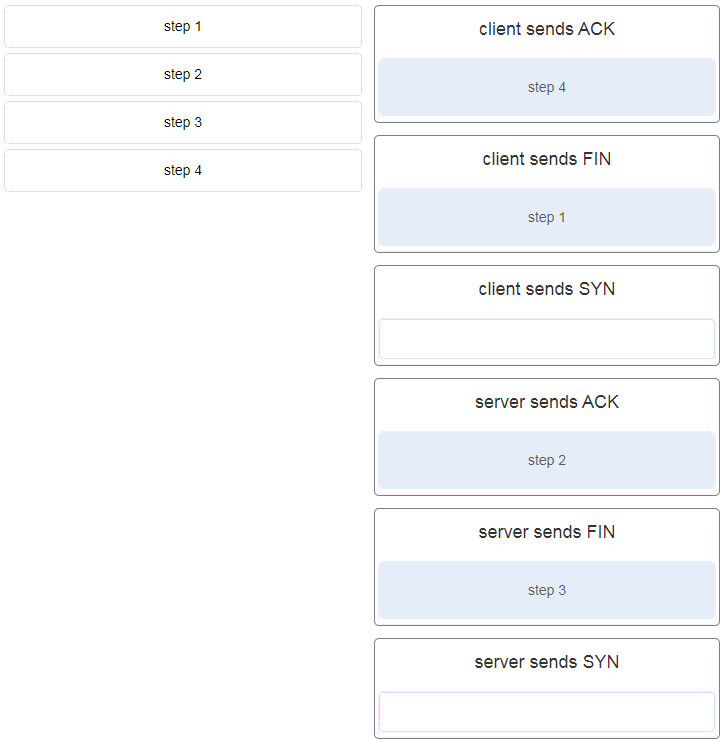
13. A client application needs to terminate a TCP communication session with a server. Place the termination process steps in the order that they will occur. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: In order to terminate a TCP session, the client sends to the server a segment with the FIN flag set. The server acknowledges the client by sending a segment with the ACK flag set. The server sends a FIN to the client to terminate the server to client session. The client acknowledges the termination by sending a segment with the ACK flag set.
14. Which flag in the TCP header is used in response to a received FIN in order to terminate connectivity between two network devices?
Explanation: In a TCP session, when a device has no more data to send, it will send a segment with the FIN flag set. The connected device that receives the segment will respond with an ACK to acknowledge that segment. The device that sent the ACK will then send a FIN message to close the connection it has with the other device. The sending of the FIN should be followed with the receipt of an ACK from the other device.
15. Which protocol or service uses UDP for a client-to-server communication and TCP for server-to-server communication?
Explanation: Some applications may use both TCP and UDP. DNS uses UDP when clients send requests to a DNS server, and TCP when two DNS serves directly communicate.
16. What is a characteristic of UDP?
Explanation: UDP has no way to reorder the datagrams into their transmission order, so UDP simply reassembles the data in the order it was received and forwards it to the application.
17. What kind of port must be requested from IANA in order to be used with a specific application?
Explanation: Registered ports (numbers 1024 to 49151) are assigned by IANA to a requesting entity to use with specific processes or applications. These processes are primarily individual applications that a user has chosen to install, rather than common applications that would receive a well-known port number. For example, Cisco has registered port 1985 for its Hot Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP) process.
18. Which three application layer protocols use TCP? (Choose three.)
Explanation: Some protocols require the reliable data transport that is provided by TCP. In addition, these protocols do not have real time communication requirements and can tolerate some data loss while minimizing protocol overhead. Examples of these protocols are SMTP, FTP, and HTTP.
19. Which three statements characterize UDP? (Choose three.)
Explanation: UDP is a simple protocol that provides the basic transport layer functions. It has much lower overhead than TCP because it is not connection-oriented and does not offer the sophisticated retransmission, sequencing, and flow control mechanisms that provide reliability.
Explanation: The sequence number and window fields are included in the TCP header but not in the UDP header.
21. Which field in the TCP header indicates the status of the three-way handshake process?
Explanation: The value in the control bits field of theTCP header indicates the progress and status of the connection.
22. Why does HTTP use TCP as the transport layer protocol?
Explanation: When a host requests a web page, transmission reliability and completeness must be guaranteed. Therefore, HTTP uses TCP as its transport layer protocol.
Explanation: Applications that can tolerate some data loss, require a simple request and reply, and handle reliability themselves are best suited for UDP. UDP has low overhead and no requirement of reliability. TCP provides services for reliability, controlling data flow, and the reordering of segments.
24. How are port numbers used in the TCP/IP encapsulation process?
Explanation: Both UDP and TCP use port numbers to provide a unique identifier for each conversation. Source port numbers are randomly generated and are used to track different conversations. Destination port numbers identify specific services by using either a default port number for the service or a port number that is assigned manually by a system administrator.
25. In what two situations would UDP be better than TCP as the preferred transport protocol? (Choose two.)
Explanation: UDP is a very simple transport layer protocol that does not guarantee delivery. Devices on both ends of the conversation are not required to keep track of the conversation. UDP is used as the transport protocol for applications that need a speedy, best-effort delivery.
26. What are three responsibilities of the transport layer? (Choose three.)
Explanation: The transport layer has several responsibilities. Some of the primary responsibilities include the following:
Tracking the individual communication streams between applications on the source and destination hosts
Segmenting data at the source and reassembling the data at the destination
Identifying the proper application for each communication stream through the use of port numbers
Multiplexing the communications of multiple users or applications over a single network
Managing the reliability requirements of applications
Explanation: When a host configured to use DHCP powers up on a network it sends a DHCPDISCOVER message. FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF is the L2 broadcast address. A DHCP server replies with a unicast DHCPOFFER message back to the host.
28. Which two protocols may devices use in the application process that sends email? (Choose two.)
Explanation: POP, POP3, and IMAP are protocols that are used to retrieve email from servers. SMTP is the default protocol that is used to send email. DNS may be used by the sender email server to find the address of the destination email server.
29. What is true about the Server Message Block protocol?
Explanation: The Server Message Block protocol is a protocol for file, printer, and directory sharing. Clients establish a long term connection to servers and when the connection is active, the resources can be accessed. Every SMB message has the same format. The use of SMB differs from FTP mainly in the length of the sessions. SMB messages can authenticate sessions.
30. What is the function of the HTTP GET message?
Explanation: There are three common HTTP message types:
31. Which OSI layer provides the interface between the applications used to communicate and the underlying network over which messages are transmitted?
Explanation: The application layer is the layer that is closest to the end user and provides the interface between the underlying network and the applications used to communicate.
32. Which networking model is being used when an author uploads one chapter document to a file server of a book publisher?
Explanation: In the client/server network model, a network device assumes the role of server in order to provide a particular service such as file transfer and storage. In the client/server network model, a dedicated server does not have to be used, but if one is present, the network model being used is the client/server model. In contrast, a peer-to-peer network does not have a dedicated server.
33. What do the client/server and peer-to-peer network models have in common?
Explanation: In both the client/server and peer-to-peer network models, clients and servers exist. In peer-to-peer networks, no dedicated server exists, but a device can assume the server role to provide information to a device serving in the client role.
34. In what networking model would eDonkey, eMule, BitTorrent, Bitcoin, and LionShare be used?
Explanation: In a peer-to-peer networking model, data is exchanged between two network devices without the use of a dedicated server. Peer-to-peer applications such as Shareaz, eDonkey, and Bitcoin allow one network device to assume the role of server, while one or more other network devices assume the role of client using the peer-to-peer application.
35. What is a common protocol that is used with peer-to-peer applications such as WireShare, Bearshare, and Shareaza?
Explanation: The Gnutella protocol is used when one user shares an entire file with another user. A person would load a Gnutella-based application such as gtk-gnutella or WireShare and use that application to locate and access resources shared by others.
Explanation: The peer-to-peer (P2P) networking model allows data, printer, and resource sharing without a dedicated server.
37. The application layer of the TCP/IP model performs the functions of what three layers of the OSI model? (Choose three.)
Explanation: The network access layer of the TCP/IP model performs the same functions as the physical and data link layers of the OSI model. The internetwork layer equates to the network layer of the OSI model. The transport layers are the same in both models. The application layer of the TCP/IP model represents the session, presentation, and application layers of the OSI model.
38. What is an example of network communication that uses the client-server model?
Explanation: When a user types a domain name of a website into the address bar of a web browser, a workstation needs to send a DNS request to the DNS server for the name resolution process. This request is a client/server model application. The eMule application is P2P. Sharing a printer on a workstation is a peer-to-peer network. Using ARP is just a broadcast message sent by a host.
39. Which layer in the TCP/IP model is used for formatting, compressing, and encrypting data?
Explanation: The application layer of the TCP/IP model performs the functions of three layers of the OSI model – application, presentation, and session. The application layer of the TCP/IP model is the layer that provides the interface between the applications, is responsible for formatting, compressing, and encrypting data, and is used to create and maintain dialogs between source and destination applications.
40. What is an advantage of SMB over FTP?
Explanation: SMB and FTP are client/server protocols that are used for file transfer. SMB allows the connecting device to access resources as if they were on the local client device. SMB and FTP use the TCP protocol for connection establishment and they can transfer data in both directions. FTP requires two connections between the client and the server, one for commands and replies, the other for the actual file transfer.
41. A manufacturing company subscribes to certain hosted services from its ISP. The services that are required include hosted world wide web, file transfer, and e-mail. Which protocols represent these three key applications? (Choose three.)
Explanation: The ISP uses the HTTP protocol in conjunction with hosting web pages, the FTP protocol with file transfers, and SMTP with e-mail. DNS is used to translate domain names to IP addresses. SNMP is used for network management traffic. DHCP ic commonly used to manage IP addressing.
Explanation: The GET command is a client request for data from a web server. A PUT command uploads resources and content, such as images, to a web server. A POST command uploads data files to a web server.
43. What type of information is contained in a DNS MX record?
Explanation: MX, or mail exchange messages, are used to map a domain name to several mail exchange servers that all belong to the same domain.
44. Which three protocols operate at the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
Explanation: FTP, DHCP, and POP3 are application layer protocols. TCP and UDP are transport layer protocols. ARP is a network layer protocol.
45. Which protocol is used by a client to communicate securely with a web server?
Explanation: HTTPS is a secure form of HTTP used to access web content hosted by a web server.
46. Which applications or services allow hosts to act as client and server at the same time?
Explanation: P2P applications allow the clients to behave as servers if needed. When using authentication services, email exchange, and client/server applications, one host acts as server and the other acts as client at all times.
Explanation: Peer-to-peer networks have decentralized resources because every computer can serve as both a server and a client. One computer might assume the role of server for one transaction while acting as a client for another transaction. Peer-to-peer networks can share resources among network devices without the use of a dedicated server.
48. Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
Explanation: The source and destination port numbers are used to identify the correct application and window within that application.
49. Which three layers of the OSI model provide similar network services to those provided by the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
Explanation: The three upper layers of the OSI model, the session, presentation, and application layers, provide application services similar to those provided by the TCP/IP model application layer. Lower layers of the OSI model are more concerned with data flow.
50. A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received two packets of data from the PC?
51. A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received three packets of data from the PC?
52. A PC that is communicating with a web server has a TCP window size of 6,000 bytes when sending data and a packet size of 1,500 bytes. Which byte of information will the web server acknowledge after it has received four packets of data from the PC?
53. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting TFTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
54. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting FTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
55. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting SSH service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
56. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting HTTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
57. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting POP3 service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
58. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting telnet service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
59. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting SNMP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
60. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting SMTP service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?
61. A client creates a packet to send to a server. The client is requesting HTTPS service. What number will be used as the destination port number in the sending packet?